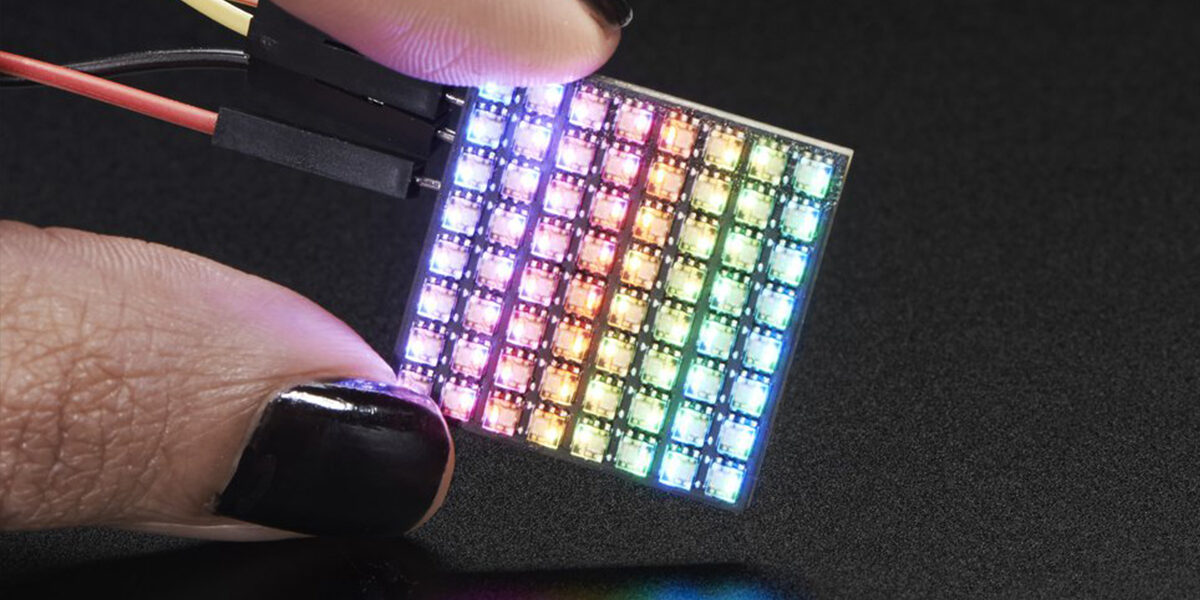
LED
(“Light Emitting Diode”) is a semi-conductor, diode based, light emitting electronic circuit element. It was invented in Russia in the 1920s and became an electronic component that could be practically applied in America in 1962. A radio technician named Oleg Vladimirovich Losev realized that the diodes used in radio receivers were emitting light, and in 1927 he published his inventions about a LED in a Russian newspaper.
At the beginning they could only give a weak red light, but contemporary LEDs can give light in high brightness in various wave lengths such as visible light, ultraviolet, infrared.
There are a number of advantages over conventional light sources such as low energy consumption, long life, stability, small size and fast opening and closing. However, it is a bit more expensive.
LED can be applied in various fields.
Features
- The LEDs are semiconductor materials.
- Main ingredients are silky.
- When the current passes through, the photon emits light by removing the light.
- They are produced to give light at different angles.
- The voltage-current graphs of the LEDs are superior. A small voltage change on the LED while in the proper operating point causes a large current change. A series current limiting resistor is connected to the LEDs to prevent distortion due to high current. This prevents deterioration of the non-sensitive LED voltage range.
- Leds drop down a constant voltage just like a Zener diode.
Also
- Red LED 2.20 Volts
- Green LED 3.30 Volts
- Blue and White LED operates with 3.40 Volt voltage.
Usage areas
RGB (Red Green Blue) lighting has been possible with the availability of blue light in LEDs and has found application in many sectors. Especially in the fields of lighting, signaling and architectural lighting, they have begun to take the place of other light sources rapidly. The most important reason for the low energy consumption of the LEDs is the low loss. In addition, these diodes, which have a very long lifetime, can be used in almost all conditions without problems because they do not carry flags like other bulbs. Some of the prototypes have reached 180 lumens / watt. Some of the prototypes have reached 180 lumens / watt. LED technology has also been used in the lighting of the Bosphorus Bridge in 2008. The LEDs display a photodiode feature on them when a frequnce light is turned off, which is the same or higher than the frequency of the light they are on. By using these features, they are also used as keys in electronic devices. They are also used in TVs and monitors.